Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Jitsi Scaling
- Implementing Jitsi Scaling with Terraform Script
- Step-by-Step Guide to Scaling Jitsi on Azure
- 1. Set Up Your Azure Environment
- 2. Install Terraform
- 3. Create Your Terraform Configuration File
- 4. Define Autoscaling Rules
- 5. Deploy Your Configuration
- 6. Monitor and Adjust
- Prerequisites for Jitsi Scaling with Terraform on Azure
- 1. Azure Subscription:
- 2. Terraform Installed:
- 3. Basic Knowledge of Terraform:
- 4. Azure CLI Installed (Optional):
- 5. Networking Knowledge:
- 6. Access to a Code Editor:
- 7. SSH Key Pair (for VM access):
- 8. Knowledge of Jitsi Components:
- Conclusion
Introduction
In a world increasingly reliant on video conferencing, Jitsi Meet stands out as a powerful open-source platform. As organizations increasingly rely on platforms like Jitsi Meet for their virtual meetings, understanding Jitsi scaling is crucial to ensure that your setup can handle varying loads efficiently. Pairing it with Terraform on Azure offers unparalleled flexibility and cost-efficiency for scaling your infrastructure. This article will guide you through the process of Jitsi scaling with Terraform script on Azure and Jitsi autoscaling enables you to optimize your infrastructure for performance and cost-effectiveness.
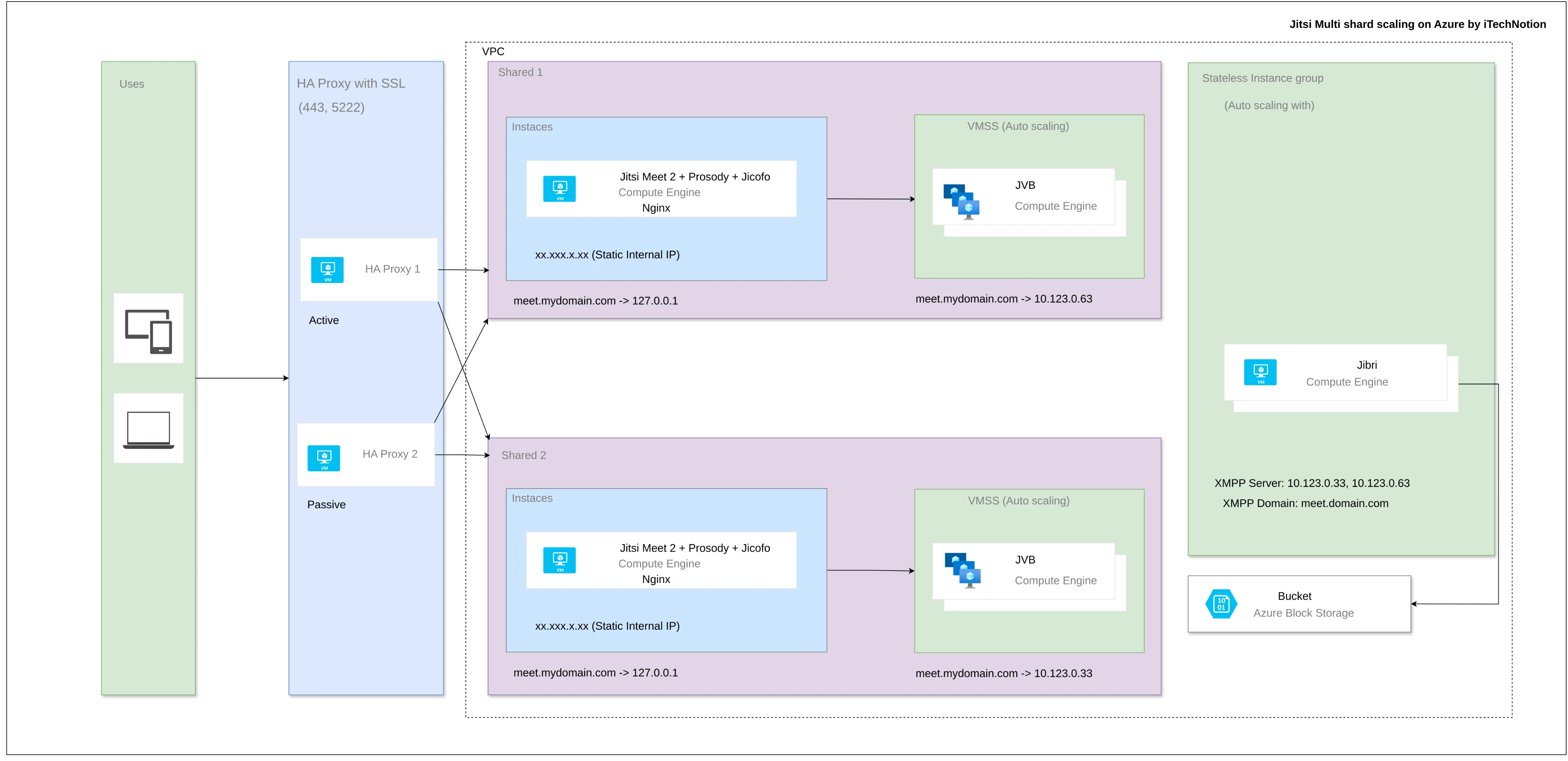
Understanding Jitsi Scaling
What is Jitsi Scaling?
Jitsi scaling refers to the process of adjusting resources in a Jitsi Meet deployment to handle fluctuating user demands. Whether you’re hosting a small team meeting or a large conference with thousands of participants, effective scaling ensures that your system remains responsive and stable.
Key Benefits of Jitsi Scaling:
- Cost Efficiency: By dynamically adjusting resources based on actual usage, you can minimize unnecessary expenses.
- Improved Performance: Scaling allows for better resource allocation during peak times, enhancing user experience.
- Flexibility: Adapting to varying loads means you can support different types of events without over-provisioning resources.
For instance, if you’re expecting a surge in users for a webinar, scaling up your resources beforehand ensures that everyone has a seamless experience.
Implementing Jitsi Scaling with Terraform Script
Why Use Terraform?
Terraform is an infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that enables you to define and manage your cloud infrastructure efficiently. Using Terraform Azure scaling script allows you to Jitsi autoscaling, deployment, and management of your Jitsi environment on Azure.
Step-by-Step Guide to Scaling Jitsi on Azure
1. Set Up Your Azure Environment
- Create an Azure account if you don’t already have one.
- Install the Azure CLI and configure it with your credentials.
2. Install Terraform
- Download and install Terraform from its official website.
- Verify the installation by running terraform -v in your command line.
3. Create Your Terraform Configuration File
- Create a new directory for your project and navigate into it.
- Create a file named [main.tf] and define your resources. Here’s a basic example:
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "jitsi_rg" {
name = "jitsi-resource-group"
location = "East US"
}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "jitsi_vnet" {
name = "jitsi-vnet"
address_space = ["10.0.0.0/16"]
location = azurerm_resource_group.jitsi_rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.jitsi_rg.name
}4. Define Autoscaling Rules
- Specify autoscaling rules based on CPU usage or other metrics to ensure that instances are added or removed as needed.
resource "azurerm_monitor_autoscale_setting" "autoscale" {
name = "jitsi-autoscale"
location = azurerm_resource_group.jitsi_rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.jitsi_rg.name
profile {
name = "autoscale-profile"
capacity {
minimum = 1
maximum = 10
default = 3
}
rule {
metric_trigger {
metric_name = "Percentage CPU"
metric_resource_id = azurerm_virtual_machine_scale_set.jitsi_vmss.id
operator = "GreaterThan"
threshold = 70
aggregation = "Average"
frequency = "PT5M"
}
scale_action {
direction = "Increase"
change_count = 1
cooldown = "PT5M"
}
}
}
}5. Deploy Your Configuration
- Run [terraform init] to initialize the directory.
- Execute [terraform] apply to create the resources defined in your configuration file.
6. Monitor and Adjust
- Use Azure Monitor to keep track of performance metrics and adjust your autoscaling rules as necessary.
By following these steps, you can effectively implement Jitsi scaling with Terraform script on Azure, ensuring that your platform can handle varying loads seamlessly.
Prerequisites for Jitsi Scaling with Terraform on Azure
To set up Jitsi scaling with Terraform on Azure, you’ll need to ensure you have the following prerequisites in place:
1. Azure Subscription:
- You must have an active Azure subscription. If you don’t have one, you can create a free account to get started.
2. Terraform Installed:
- Download and install Terraform on your local machine. You can find installation instructions on the Terraform website. After installation, verify it by running terraform -version in your command line.
3. Basic Knowledge of Terraform:
- Familiarity with Terraform concepts, such as providers, resources, and state management, will help you effectively manage your infrastructure.
4. Azure CLI Installed (Optional):
- While not strictly necessary, having the Azure CLI installed can be beneficial for managing Azure resources directly from the command line.
5. Networking Knowledge:
- Understanding basic networking concepts is helpful, as you’ll need to configure virtual networks and subnets for your Jitsi deployment.
6. Access to a Code Editor:
- A code editor (like Visual Studio Code or any text editor) will be necessary for writing and editing your Terraform configuration files.
7. SSH Key Pair (for VM access):
- If you’re planning to access your virtual machines via SSH, create an SSH key pair for secure access to the VMs.
8. Knowledge of Jitsi Components:
- Familiarity with Jitsi architecture (including components like Jitsi Videobridge, Prosody, and Jicofo) will help in configuring and scaling the setup effectively.
By ensuring these prerequisites are met, you will be well-prepared to automate and scale your Jitsi deployment using Terraform on Azure efficiently.
Conclusion
Understanding Jitsi scaling is vital for any organization looking to leverage video conferencing effectively. By implementing strategies such as using a Terraform script on Azure, you can ensure that your setup is not only efficient but also cost-effective.
Have you ever struggled with managing fluctuating loads during virtual events? You can schedule a meeting with our expert.
Related articles:
How to set up Jitsi Meet on GCP using Terraform?
How to set up Jitsi Meet on AWS using Terraform?
FAQ
You can set up Jitsi Meet on Azure by creating a Terraform configuration file, defining the necessary resources, and deploying it using Terraform apply.
Use autoscaling rules in Azure to dynamically adjust resources based on user demand, ensuring optimal performance during large conferences.
Define autoscaling rules in your Terraform configuration file based on metrics like CPU usage, and deploy them with Azure Monitor for real-time adjustments.
Implement dynamic autoscaling to allocate resources only when needed, avoiding unnecessary expenses during low-usage periods.
Use Azure Monitor to track performance metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and user activity, to make necessary adjustments.
Download Terraform from its official website, install it, and verify the installation using the terraform -v command.
Use the main.tf file to specify resources like resource groups, virtual networks, and scaling rules in your Azure environment.
Update your Terraform configuration file with new rules and reapply using terraform apply to modify the deployed setup.
Pre-scale your resources by temporarily increasing instance limits or setting up autoscaling rules to handle the expected load.
Use multi-region deployments and geo-distributed servers on Azure to reduce latency and improve accessibility for users worldwide.